Boost Your Career with the Best Cybersecurity Certifications in 2025
Boost Your Career with the Best Cybersecurity Certifications in 2025

Dive into the 2025 cybersecurity certification landscape with this guide—packed with actionable insights, the latest industry data on talent gaps and breach costs, and AI-informed career direction to help you stay ahead.
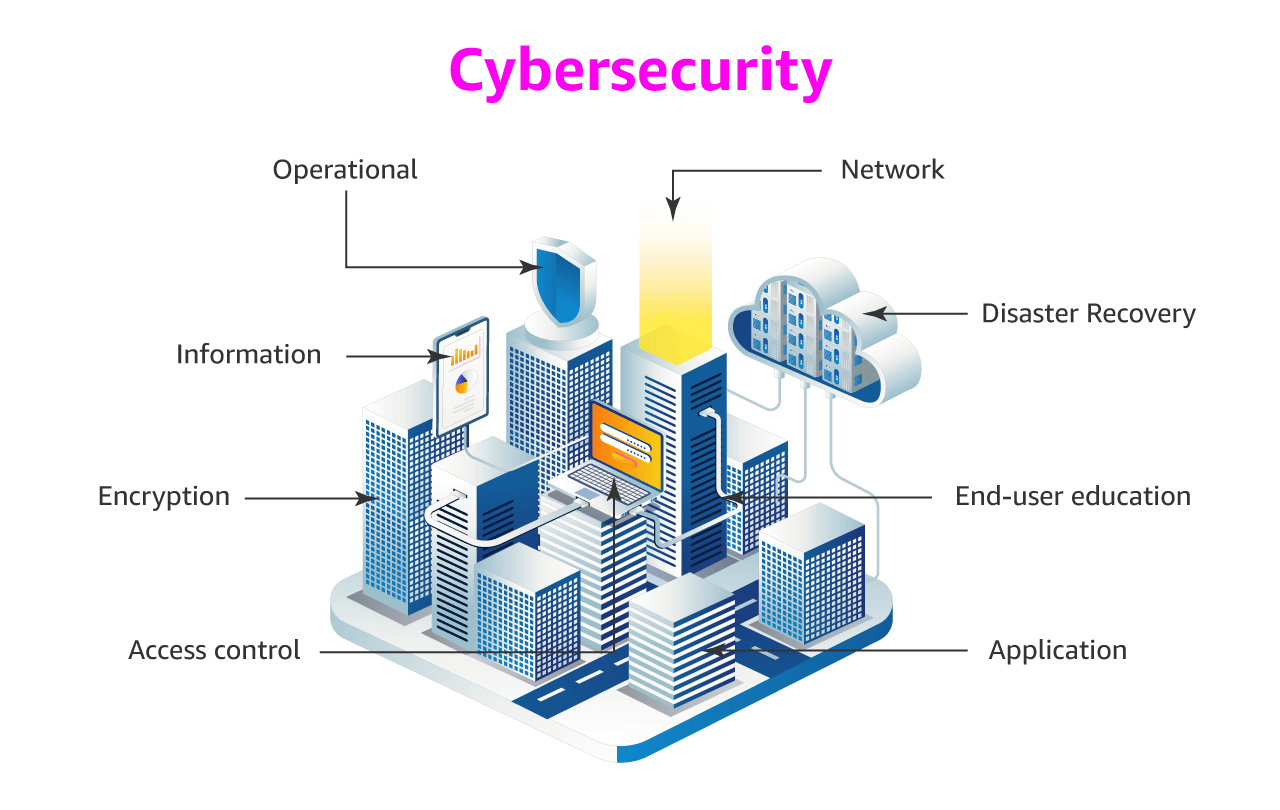
Top Cybersecurity Skills in 2025: Your Top Business Imperative.
In a digital-first world, cybersecurity has evolved from IT overhead to a board-level mission-critical priority. Here’s what you must know now:
- Global talent shortfall: The cybersecurity workforce gap has surged to 4.8 million vacant roles worldwide, a 19% increase year-on-year. Organizations suffering from this skills shortage face $1.76 million higher average breach costs.
- Breach costs remain staggering: The average cost of a data breach globally soared to $4.88 million in 2024, a 10% uptick year-over-year. U.S. organizations typically incur well over $5 million in costs per breach.
- Cybercrime’s economic footprint: Global cybercrime is projected to cost businesses $10.5 trillion in 2025, and may reach $15.6 trillion by 2029.
- AI is the new cyber battleground: Nearly 87% of organizations experienced an AI‑powered cyber attack in the last year. Generative AI is being used to craft highly persuasive phishing lures and deepfake scams—while also empowering defenders to act faster and more accurately.
Why It Matters Now
Cybersecurity isn’t just about tech—it’s about trust, business continuity, and protecting revenue. Here’s why investing in cybersecurity training and certifications matters now:
Certified professionals bridge that talent gap, accelerating response times and reducing dwell time—the time attackers remain undetected in networks—directly translating to lower breach costs.
Certifications reassure stakeholders—from CEOs to clients—that your team uses validated strategies proven to mitigate AI-enabled, sophisticated threats.
Why Cybersecurity Certifications Matter in 2025 and beyond.
High Employer Trust in Certifications: In 2025, 47% of hiring managers rated cybersecurity certifications as more critical than IT experience, and 90% would equally consider candidates with only foundational cybersecurity certifications like ISC²’s Certified in Cybersecurity (CC) or CompTIA Security+.
Productivity & Quality Gains: According to GIAC, 72% of certified professionals report higher productivity, 81% enhanced work quality, 74% greater autonomy, and 77% more innovation—making certification a clear performance lever.
Severe Workforce Crunch: This year, the global cybersecurity workforce plateaued at 5.5 million, but the overall gap ballooned to 4.8 million unfilled roles—a 19% increase from 2023, showing just how urgent certification is as a career differentiator.
Certification Drives Career Momentum: Within six months of earning a CompTIA certification, 91% of professionals reported advancing at least one career step—whether through better job placements, promotions, or expanded responsibilities.
Why This Matters
- Certified professionals stand out: Certifications validate your skillset and serve as proof of readiness to meet high-stakes security challenges.
- Certification drives workplace performance: Boosted productivity, autonomy, and innovation turn certified teams into strategic business assets.
- Certification bridges talent gaps: In the face of acute workforce shortages, certified individuals are the fastest way to fill crucial roles with trusted professionals.
Top 5 Jobs To Explore After Obtaining a Cybersecurity Certification
Have you been thinking of getting into cybersecurity? Here are a few cybersecurity career paths you could potentially explore.
1. IT Auditor:
The IT auditor role is a stepping stone for those advancing in their cybersecurity careers, particularly for those aiming to become cybersecurity analysts or engineers. As an IT auditor, you’ll play a crucial role in ensuring IT systems adhere to established policies and practices. Your responsibilities will include evaluating technology, managing teams, identifying necessary controls, and maintaining comprehensive records.
Average salary: ranges from 90,468 to RM159,365.
2. Chief Information Security Officer (CISO):
The chief information security officer, or CISO, is the executive responsible for an organization’s data and cybersecurity needs.
A chief information security officer is expected to develop the processes and plans that are needed to protect critical systems and safeguard data. These leaders should have wide-ranging knowledge of IT infrastructure and cybersecurity procedures and practices to help enable secure operations. Effective CISOs lead a team of cybersecurity professionals to implement safe data practices and safeguard business functions.
Average salary: ranges from RM173,147 to RM311,664.
3. Cybersecurity architect:
A cybersecurity architect plays a vital role in protecting an organization’s systems, networks, and sensitive data from cyber threats. They design, implement, and manage a robust security infrastructure while ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations.
By assessing risks and integrating advanced security measures, cybersecurity architects strengthen an organization’s defenses and maintain a secure IT environment.
Average salary: ranges from RM189,560 to RM234,697.
4. Information security analyst:
This individual employs analytics is in charge of the company’s computer systems and networks. They employ analytics to find holes in a firm’s data security system and protect sensitive and private data.
Given their extensive range—detecting, analyzing, and dealing with data theft and cyberattacks—data security analysts are the gatekeepers or security officers of information management.
Average salary: ranges from RM93,146 to RM158,034.
5. Forensic investigator:
Analysts specializing in computer fraud identify hacking attacks and conduct audits to stop new ones. Forensic accounting uses computer inquiry and analysis tools to determine probable legal evidence.
Information may be sought concerning various misuses or computer crimes, including but not limited to business secret theft, the theft or destruction of intellectual property, and fraud. CHFIs use multiple techniques to find and recover lost, encrypted or corrupted file information.
Average salary: ranges from RM77,223 to RM134,339.
6. Cybersecurity Engineer
In today’s digital age, businesses and individuals are more connected than ever before, relying heavily on technology for various aspects of life. This increased connectivity also means that cyber threats are on the rise, making the need for effective cybersecurity measures more critical.
One of the key players in ensuring the safety and integrity of digital assets is the cybersecurity engineer.
A cybersecurity engineer is a professional who specializes in designing, implementing, and maintaining secure systems to protect organizations from cyber threats. These engineers play a vital role in safeguarding sensitive data, intellectual property, and other digital assets from unauthorized access, theft, or destruction.
With a need for 4.6 million cybersecurity professionals in the U.S. alone, there is a huge demand for Cybersecurity Engineers
Average salary: ranges from RM110,900 to RM195,357.
The income of cybersecurity professionals is expected to expand by 33% between 2020 and 2030. 16,300 job opportunities are estimated each year for data security specialists within the next decade.
Open the door to your cybersecurity career with our top cybersecurity certifications for 2025.
AWS Certified Security – Specialty
Today’s cloud technology is transforming security from an inhibitor of progress into a critical enabler of success. Learning to understand and apply the latest security best practices allows you to do more in the cloud—helping you stand out among your peers and driving new career opportunities.
This credential helps organizations identify and develop talent with critical skills for implementing cloud initiatives. Earning AWS Certified Security – Specialty validates expertise in securing data and workloads in the AWS Cloud.
| Course Code | Course Title | Days | Fees (RM) | Oct-25 | Nov-25 | Dec-25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWS-SEC | Security Engineering on AWS | 3 | 5,400 | – | 19-21 | – |
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
Earning the CISSP credential proves you have what it takes to effectively design, implement and manage a best-in-class cybersecurity program. With a CISSP, you validate your expertise and become an (ISC)² member, unlocking a broad array of exclusive resources, educational tools, and peer-to-peer networking opportunities.
The best candidates for the CISSP are skilled cybersecurity experts in the C-suite, including chief information officers and architects and analysts. If the CISSP is not for you, (ISC)2 also offers the CCSP for Cloud Security and the HCISPP for Healthcare Security & Privacy. CCSP for Cloud Security and HCISPP for Healthcare Security & Privacy are a couple of the certifications that (ISC)2 provides if the CISSP isn’t for you.
| Course Code | Course Title | Days | Fees (RM) | Oct-25 | Nov-25 | Dec-25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CISSP | Certified Information System Security Professional Prep Course | 5 | 8,500 | 6-10 | 24-28 | 1-5 |
Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
ISACA’s Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) certification indicates expertise in information security governance, program development and management, incident management and risk management. If you are a mid-career IT professional aspiring to senior management roles in IT security and control, CISM can get you the visibility you need.
The CISM certification, also provided by ISACA, allows you to prove your expertise on the management side of information security, covering governance, program building, and program, incident, and risk management. You must have 5 years of experience in information security management to sit for the CISM exam. As part of this criterion, you must have up to two years of general information security experience.
| Course Code | Course Title | Days | Fees (RM) | Oct-25 | Nov-25 | Dec-25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CISM | Certified Information Security Manager | 4 | 9,000 | 27-30 | 10-13 | 8-11 |
The CompTIA Security+ credential is a global certification that validates the baseline skills necessary to perform core security functions and pursue an IT security career. It is the first security certification a candidate should earn. It establishes the core knowledge required of any cybersecurity role and provides a springboard to intermediate-level cybersecurity jobs.
For professionals in the tech sector, CompTIA is a pioneer in certification. Many organizations look for candidates with the CompTIA Security+ certification, and more businesses choose this certification than any other one.
| Course Code | Course Title | Days | Fees (RM) | Oct-25 | Nov-25 | Dec-25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT-Security+ | CompTIA Security+ | 5 | 3,500 | – | 10-14 | – |
CompTIA’s Advanced Security Practitioner Certification (CASP+) is now the new CompTIA SecurityX, the latest addition to CompTIA’s Xpert series. SecurityX is the capstone certification in CompTIA cybersecurity pathway, and it’s designed for experts in the field, like you, who are ready to advance in their career.
Targeted at professionals with 5 to 10 years of experience, SecurityX represents the pinnacle of cybersecurity certifications. It is specifically designed for senior security engineers and security architects tasked with leading and improving an enterprise’s cybersecurity readiness.
| Course Code | Course Title | Days | Fees (RM) | Oct-25 | Nov-25 | Dec-25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT-CSX | CompTIA SecurityX | 5 | 4,500 | – | 24-28 | – |
Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate
The Azure Security Engineer Associate certification validates that you have subject matter expertise implementing security controls and threat protection, managing identity and access, and protecting data, applications, and networks in cloud and hybrid environments as part of an end-to-end infrastructure. You earn this certification by passing Exam AZ-500: Microsoft Azure Security Technologies.
If your responsibilities as part of a larger team include maintaining the security posture, identifying and remediating vulnerabilities by using a variety of security tools, implementing threat protection, and responding to security incident escalations, this could be the certification for you.
| Course Code | Course Title | Days | Fees (RM) | Oct-25 | Nov-25 | Dec-25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AZ-500T00 | Microsoft Azure Security Technologies | 4 | 3,000 | – | – | 1-4 |
Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
The CISA certification by ISACA is world-renowned as the standard of achievement for those who audit, control, monitor and assess an organization’s information technology and business systems. The recent quarterly IT Skills and Certifications Pay Index (ITSCPI) from Foote Partners ranked CISA among the most sought-after and highest-paying IT certifications. This certification is a must have for entry to mid-career IT professionals looking for leverage in career growth.
The Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) was created for security auditors who work professionally and want to demonstrate their knowledge. This certification covers various topics, including information system creation, asset protection, auditing procedures, and governance. Entry-level to mid-level workers with a foundational understanding of information systems are best suited for the CISA. Many exam preparation resources are available for those interested in this certification, including manuals and online refresher courses.
| Course Code | Course Title | Days | Fees (RM) | Oct-25 | Nov-25 | Dec-25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CISA | Certified Information Systems Auditor | 5 | 9,500 | 13-16 | 3-7 | – |
Microsoft Certified: Security Operations Analyst Associate
Whether you’re a business stakeholder, new or existing IT professional, or a student who has an interest in Microsoft security, compliance, and identity (SCI) solutions, this certification can help you familiarize yourself with the fundamentals of SCI across cloud-based and related Microsoft services.
The Microsoft Security Operations Analyst collaborates with organizational stakeholders to secure information technology systems for the organization. Their goal is to reduce organizational risk by rapidly remediating active attacks in the environment, advising on improvements to threat protection practices, and referring violations of organizational policies to appropriate stakeholders.
| Course Code | Course Title | Days | Fees (RM) | Oct-25 | Nov-25 | Dec-25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC-200T00 | Microsoft Security Operations Analyst | 4 | 3,000 | – | 10-13 | 15-18 |
RCCE1: Rocheston Certified Cybersecurity Engineer – Level 1
Cybersecurity is a constantly evolving and highly volatile space in the contemporary world.
Packed with fascinating possibilities, this is a domain that is waiting to explode into the world any moment now. To face the various emerging threats in the cyberworld, cybersecurity engineers need to prepare themselves with adequate knowledge and expertise.
This is where Rocheston comes in. The Rocheston RCCE cybersecurity certifications will enable you to become certified specialists in the various fields within the budding discipline of cybersecurity.
The RCCE Level 1 covers the foundational concepts of hacking. This course will give you a detailed, in-depth knowledge and hands-on labs. You will have mastery over hacking technologies and tools and RCCE Certification is accredited by ANSI, which means the RCCE credential is now internationally recognized around the world.
| Course Code | Course Title | Days | Fees (RM) | Oct-25 | Nov-25 | Dec-25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCCE 1 | Rocheston Certified Cybersecurity Engineer – Level 1 | 5 | 6,500 | – | 3-7 | – |
Conclusion
Cybersecurity threats are becoming more and more sophisticated as time goes on. The best way to protect your organization from these threats is by ensuring all your employees are cybersec-trained. This will help them understand how to identify potential attacks, and how to protect your systems from them.
Which is why cybersecurity skills and experience are important because they provide the training and tools needed to protect your organization from cyberthreats. Identify potential threats, prevent them from happening, and respond to threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Cybersecurity Certifications Should I Get First?
Choosing your first cybersecurity certification can feel overwhelming. That’s why it’s best to go with a widely respected industry standard like CompTIA Security+ that covers the fundamentals of cybersecurity.
More than half a million information technology pros have earned CompTIA Security+. There are several reasons for the certification’s popularity:
- It is respected both industry-wide and globally. Employers know who CompTIA is. Because of this, CompTIA Security+ will add weight to your resume and give you immediate credibility with employers.
- It is an entry-level cybersecurity certification. This makes it perfect for beginners without prior IT or work experience.
- There are no prerequisites required for CompTIA Security+. That’s why it is an ideal first cybersecurity certification to earn.
- It is vendor-neutral. Vendor-neutral certifications apply to any type of equipment. They provide foundational skills technicians need to successfully earn vendor-specific cybersecurity certifications in the future. These designations give IT pros the diverse skill set employers want to see.
What Certifications Do You Need for Cybersecurity?
Getting started in cybersecurity can be a challenge, despite the fact that job vacancies abound. The right entry-level certification makes it much easier to start your cybersecurity career. But which beginner-level credential is best for you?
- Entry-Level Certification Options (CompTIA Security+, ISACA CISM)
- Penetration Testing Certification Options (CompTIA PenTest+)
- Senior-Level Cybersecurity Certifications (CompTIA CASP+, CISSP)
Exploring for more beginner-friendly certifications other than cybersecurity?
If you’re new to the field of IT and seeking a beginner-friendly guide, don’t miss our blog post on the “Top IT Certifications for Beginners.” This comprehensive guide is designed to help you confidently begin your journey into the world of IT certifications.
Maximize the benefits of these informative blogs to boost your IT career. Happy learning!